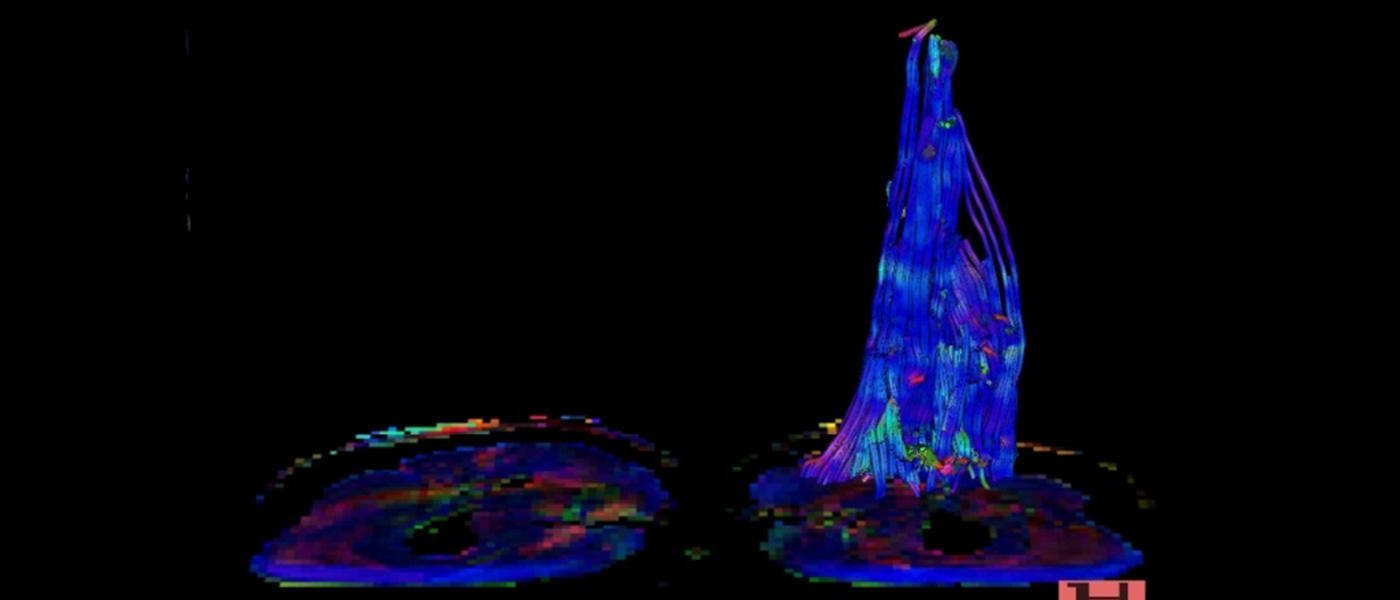
Non-enhanced MRCP with breath-triggered technique
MRCP - Non-invasive Diagnosis of Hepatobiliary System
Optimization and Development of Cholangiopancreatography
The magnetic resonance choloangiography (MRCP) is a relative new, non-invasive technique for simultaneous visualisation of hepatic and pancreatic duct system. A high contrast between non.mobile fluid for e.g. in gall bladder and the surrounding parenchymatous organs is achieved through use of high T2-weighted sequence protocols. A number of sequences like gradient echo or turbo spin echo sequences can be used to achieve this. This is further improved with the use different techniques like breath hold technique, breath-triggered and application of oral contrast.
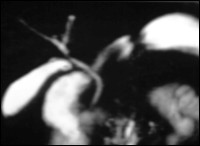
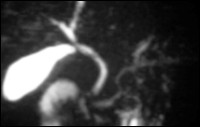
MRCP with oral contrast
Standard Protocol
A strong T2-weighted sequence with inverse recovery is used to visualise the hepatobiliary duct system. Thin slices in coronal orientation using 3D measurements are used for complete visualisation of a large volume. 3D-MIP (maximum intensity projection) reconstruction are made from the raw image data after the examination.
Oral contrast enhanced MRCP
For better anatomical visualisation and assessment of the biliary system the patient is given an oral superparamagnetic, negative contrast media (300 ml Lumirem®). With this technique the high signal due to fluid content in the stomach and intestine is neutralised which allows detailed and better assessment of the peripheral biliary ducts and pancreatic duct. This sequence protocol can also be used in transverse imaging for better anatomical orientation.
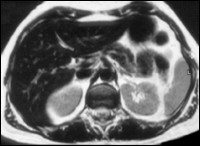
T2-TSE after oral contrast media
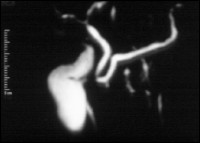
Respiration triggered MRCP post oral contrast media
MRCP in Breath-Hold Technique
It is possible to visualise the whole biliary system within seconds in a single thick slice (10 cm) using the HASTE-sequence. This new sequence allows immediate and accurate non-invasive over view of the hepatobiliary system without reconstruction. The use of this protocol in different projections allows a speedy and accurate evaluation of different possible pathologies. The following methods can be used as orientation for better planning of MRCP:
Functional MRCP
The use of consecutive fast and modified HASTE-sequence allows acquisition of functional data for dynamic evaluation of the biliary system.
Combined MRT-MRCP-MRA Examination
The use of native and contrast enhanced sequences (MRI) to diagnosis of parenchyma and the vascular system (MRA) are available as additional options.
T2-TSE post oral contrast media
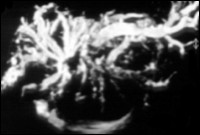
MRCP
Klatskin Tumor
T1-GRE post i.v. Gd-DTPA
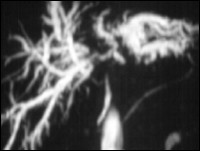
MRCP
Stenosis of the Anastomosis post liver transplantation
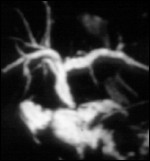
Respiration triggered MRCP
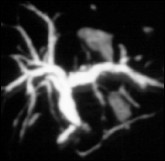
Respiration triggered MRCP, post oral contrast media
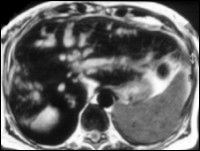
Carcinoma of body of Pancreas
Documentation of a signal-loss with poststenotic dilatation of pancreatic duct in body of pancreas in MRCP. Visualisation of a hypointense mass in T1 weighted GRE-sequence which corresponds to carcinoma of pancreas.
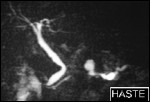
HASTE MRI
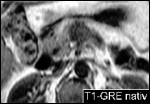
Non-enhanced T1W-GRE
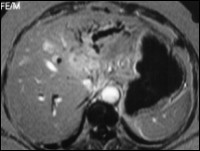
Carcinoma of Tail of Pancreas
Visualiastion of a signal-loss in pancreatic duct in tail of pancreas in MRCP with poststenotic dilatation, corresponding to carcinoma of pancreas.
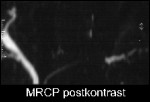
MR subtraction image post contrast media
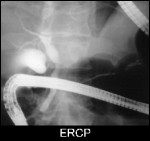
Conventional ERCP
Chronic Pancreatitis
Continuous dilatation of pancreatic duct with calcifications in branches suggesting chronic pancreatitis in the MRCP.
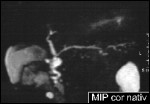
MR subtraction image of pancreatic duct
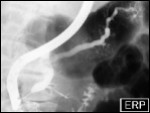
Conventional visualisation of pancreatic duct